System reliability, uptime and downtime measures are core to industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas pipeline. Reliability measurement also plays an important role for consumer-oriented services such as gas stations, ATMs, and electric charging stations. Measuring these inter-related measures helps us check system’s health, identify bottlenecks, and offer us areas of opportunity to enhance customer satisfaction.
Data collection for Predictive Analytics
System reliability is measured as weekly/monthly percentage uptime of equipment. It is a high-level indicator of system’s health. A system is said to be performing well if it reliability numbers are high and don’t fluctuate significantly over a period of time.
Uptime is generally calculated by aggregating the durations when equipment is available and/or busy. Downtime, in a similar fashion, is calculated by aggregating the durations when equipment is not available due to planned or unplanned outages. One can consider uptime and downtime as two sides of a coin.
Downtime and uptime calculations also find usage in maintenance operations. Equipment with high downtime results in high onsite inspection, part replacement, and repair cost. A ‘down’ equipment results in increasing load/demand at other equipment in vicinity, causes demand and supply imbalance and longer waiting time. Analyzing downtimes enables a system operator to determine adherence to SLAs promised to customers.
An asset maintenance system records status of every equipment and part using various labels such as óffline’and unavailable’ when an equipment is down. Duration of these statuses and critical information such as fault codes, start time, end time is archived. Downtime calculations will help us identify equipment that have:
- significantly high downtime
- low time between failures
- low time between critical failures
- fluctuating downtime
Downtime calculations will help us identify locations that face frequent and/or longer downtimes. System operator will have insights on the equipment manufactures that suffer significant downtime.
Measuring downtime is the first step towards establishing a solid foundation for preventive and predictable maintenance. Investment in preventive maintenance will help us minimize the cost of inspections, plan maintenance activities ahead of time. One will be able to schedule time consuming maintenance activities optimally and increase system reliability. Investment in predictive maintenance will help us determine the root cause of unplanned outages and identify parts that fail often. Attributing downtime to detection stage and fault codes will help us communicate better with end users, equipment manufacturers.
This approach allows us to know the fault codes that are critical and cause downtime. This is the first benefit of analysis of equipment’s data. Error codes have been categorized using attributes listed below. We have further identified operating profile attributes of a device port that are useful in helping us predict failures.
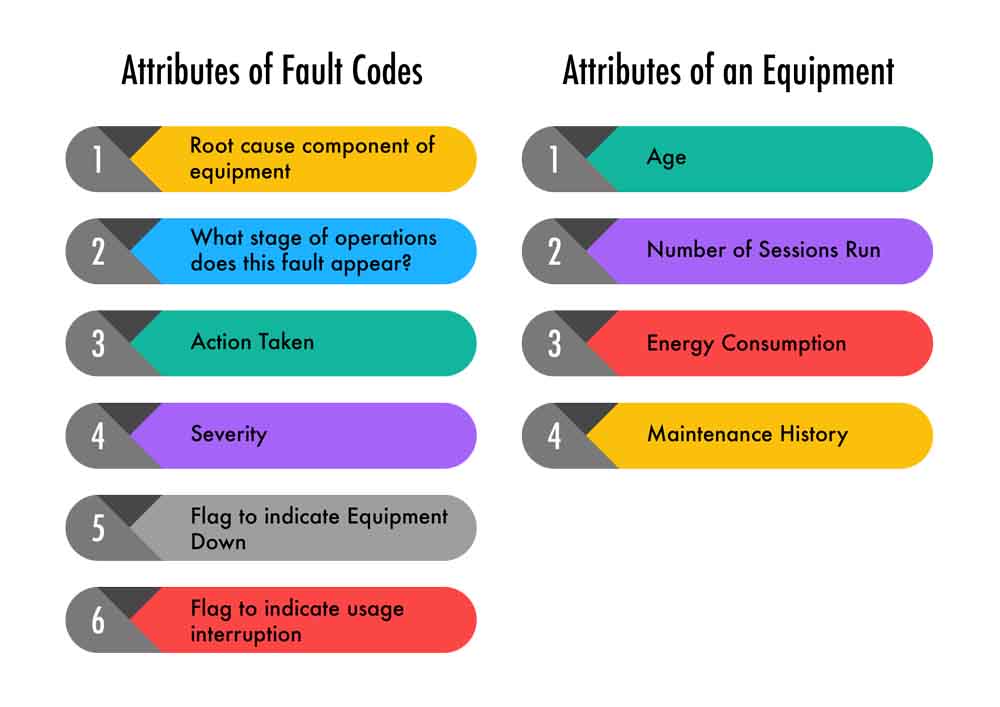
This categorization allows us to store data in a way that a solid foundation of predictive maintenance is laid out.
How does Predictive maintenance help?
- Know the failures, parts to focus on. These parts and/or failures will be the one affecting servicing cost, downtime, warranty cost.
- Pinpoint stages during equipment lifecycle where unplanned outages occur.
- Determine right servicing cost because we would know the parts that fail frequently and error codes that result in onsite inspection.
- Identify if downtime is due to network communication or external issue. It is not the equipment or part wear and tear sometimes. Failures are also caused by external events such as user’s actions.
- Know if there are more problems on input current and voltage or output current and voltage.
- Understand the age of equipment when certain failure occurs. This would help equipment manufacturers determine the right warranty cost.
- Label equipment manufacturers with reliability numbers, warranty cost, services cost.
- Eventually, it would help manufacturers design better equipment.
Optimizing Asset Maintenance
It is true that scope of predictive maintenance does not start and end with analytics. Success of predictive maintenance program is dependent on investment in historical data causing downtime or sub optimal performance. Asset maintenance discipline brings in reduced downtime, increased equipment utilization, reduced onsite inspection and repair cost, and increased system reliability.
Calculating your ROI is a difficult task when it comes to predictive analytics, but implementing the right road map for predictive maintenance can reap rewards. Reach out to us to understand more.

